What is MVP
- View is a layer that displays data and reacts to user actions. On Android, this could be an Activity, a Fragment, an android.view.View or a Dialog.
- Model is a data access layer such as database API or remote server API.
- Presenter is a layer that provides View with data from Model. Presenter also handles background tasks.
On Android MVP is a way to separate background tasks from activities/views/fragments to make them independent of most lifecycle-related events. This way an application becomes simpler, overall application reliability increases up to 10 times, application code becomes shorter, code maintainability becomes better and developer’s life becomes happier.
Why MVP on Android
Reason 1: Keep It Stupid Simple
If you haven’t read this article yet, do it: The Kiss Principle
- Most of the modern Android applications just use View-Model architecture.
- Programmers are involved into fight with View complexities instead of solving business tasks.
Using only Model-View in your application you usually end up with “everything is connected with everything”.
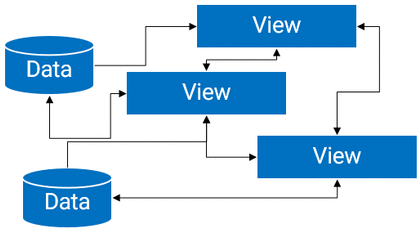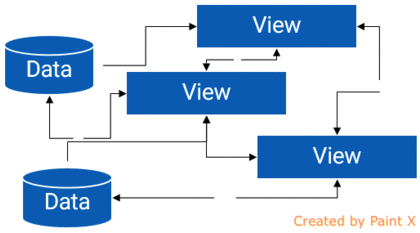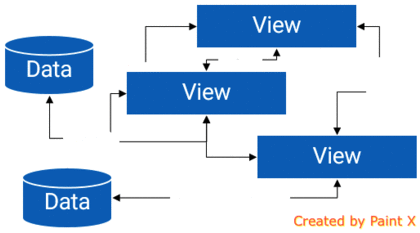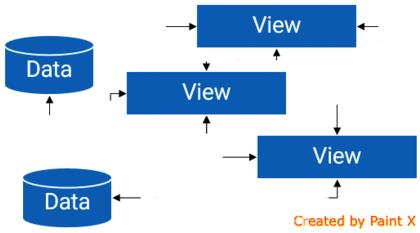
If this diagram does not look complex, then think about each View can disappear and appear at random time. Do not forget about saving/restoring of Views. Attach a couple of background tasks to that temporary Views, and the cake is ready!
An alternative to the “everything is connected with everything” is a god object.

A god object is overcomplicated; its parts cannot be reused, tested or easily debugged and refactored.
With MVP
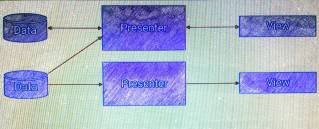
- Complex tasks are split into simpler tasks and are easier to solve.
- Smaller objects, less bugs, easier to debug.
- Testable.
View layer with MVP becomes so simple, so it does not even need to have callbacks when requesting for data. View logic becomes very linear.
Reason 2: Background tasks
Whenever you write an Activity, a Fragment or a custom View, you can put all methods that are connected with background tasks to a different external or static class. This way your background tasks will not be connected with an Activity, will not leak memory and will not depend on Activity’s recreation. We call such object “Presenter”.
There are few different approaches to handle background tasks but non of them are as reliable as MVP is.
Why this works
Here is a little diagram that shows what happens with different application parts during a configuration change or during an out-of-memory event. Every Android developer should know this data, however this data is surprisingly hard to find.
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3
|A configuration| An activity | A process
| change | restart | restart
---------------------------------------- | ------------- | ------------ | ------------
Dialog | reset | reset | reset
Activity, View, Fragment | save/restore | save/restore | save/restore
Fragment with setRetainInstance(true) | no change | save/restore | save/restore
Static variables and threads | no change | no change | reset
Case 1: A configuration change normally happens when a user flips the screen, changes language settings, attaches an external monitor, etc. More on this event you can read here:configChanges.
Case 2: An Activity restart happens when a user has set “Don’t keep activities” checkbox in Developer’s settings and another activity becomes topmost.
Case 3: A process restart happens if there is not enough memory and the application is in the background.
Conclusion
Now you can see, a Fragment with setRetainInstance(true) does not help here – we need to save/restore such fragment’s state anyway. So we can simply throw away retained fragments to limit the number of problems.
|A configuration|
| change, |
| An activity | A process
| restart | restart
---------------------------------------- | ------------- | -------------
Activity, View, Fragment, DialogFragment | save/restore | save/restore
Static variables and threads | no change | reset
Now it looks much better. We only need to write two pieces of code to completely restore an application in any possible case:
- save/restore for Activity, View, Fragment, DialogFragment;
- restart background requests in case of a process restart.
The first part can done by usual means of Android API. The second part is a job for Presenter. Presenter just remembers which requests it should execute, and if a process restarts during execution, Presenter will execute them again.
You can see complete code here.
Also you can see how to make Model View Presenter on Android here.



